TEMES 1.0
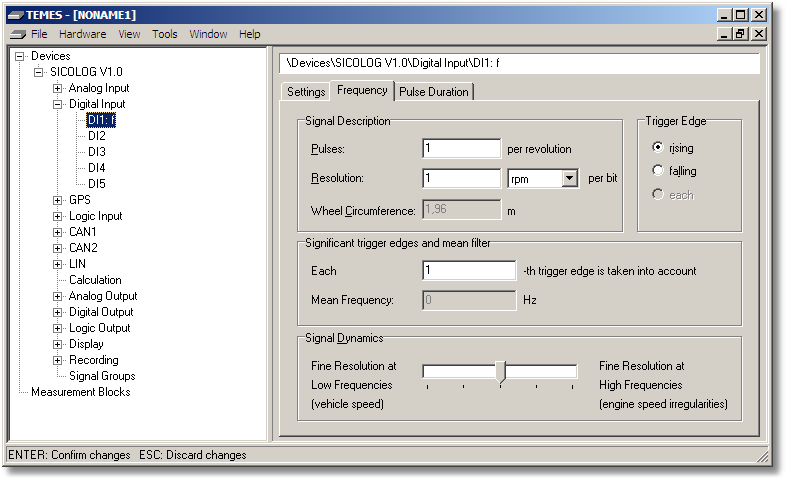
Figure 2-19: Parameter tree node Digital Input (Frequency tab).
Pulses: Number of pulses per revolution.
Resolution: Resolution per bit of the resulting frequency signal. Note that frequency signals are represented by 16-bit-values. Therefore, the maximum frequency is received by Resolution Per Bit times 65535.
Wheel Circumference: Wheel circumference in meters.
Trigger Edge: Selection whether the signal should be triggered at rising edges or falling edges.
Significant trigger edges: The significant trigger edges are a means to trigger only at a certain number of trigger edges. This is useful e. g. if you have a 7 teeth wheel with uneven teeth, you might want to trigger only at the 7th trigger edge to obtain a smooth signal.
Signal Dynamics: Defines the most important frequency range of interest. This frequency range will be quantized in smaller steps than the less important ones. Moving the wheel to the left side sets the focus on low frequencies (like vehicle speed). Whereas moving the wheel to the right side sets the focus on high frequencies (like engine speed irregularities).