TEMES 1.0
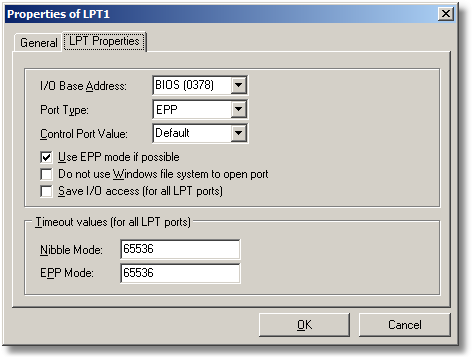
Figure 2-54: Port properties (LPT Properties tab).
The LPT properties are only supported by a 32-bit Windows Edition. A USBAD can be used instead an LPT port if the Windows Edition is 64-bit.
I/O Base Address: Hexadecimal base address of the interface unit. The entry BIOS is a placeholder for that base address which is given by the BIOS for the corresponding LPT port.
Port Type: Type of the LPT port (Standard, EPP or ECP).
Control Port Value: Hexadecimal initial value for the control register of the LPT port. If a bidirectional port is wanted to be run in uni-directional mode (e. g. for the parallel adapter PAD), the data pins must be used as outputs instead of inputs. This can be done by using the corresponding (manufacturer dependent) value for the control register (which is hexadecimal 0416 or 4416 in most cases).
Use EPP mode if possible: Uncheck this setting if an EPP transmission mode is not wanted. Note: Some ECP do not support the EPP mode.
Do not use Windows file system to open port: This item has always to be checked if the status of the corresponding port indicates that the port is used and if no application uses this port at the moment.
Save I/O access: A save I/O access is done indirectly via the HAL (= hardware abstraction layer) of Windows. A save I/O access takes more time than a direct one.
Timeout value: These values define the initial value of the timeout counters for data transmission via an LPT port. If the computer does not react instantly after updating a free LPT port, the corresponding timeout value may be reduced. On the other hand, if the data transmission fails often, the timeout value may be too low. In this case, a higher timeout value should be used.